Ecological and Socio-Economic Benefits of Spiders
Our Friendly Neighborhood Spiders
by Deborah Uson
Imagine this: a spider in a matchbox, a piece of stick from a dried coconut leaf, and a group of youngsters. What do you get? A starter pack for spider fighting—a favorite pastime among the youth in some rural and peri-urban areas in the country.
Our penchant for spider fighting and the depiction of spiders in the Philippine media is a testament that spiders have long been part of Filipino culture. This could be attributed to spiders being easily found in the neighborhood, including in small-scale urban green spaces.
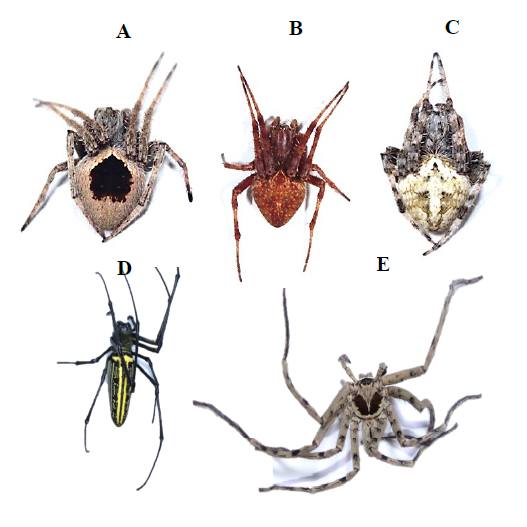
The paper “Local Community Perceptions of the Ecological and Socio-Economic Benefits of Spiders in Small-Scale Urban Green Spaces for Conservation Reinforcement” by UPMin researchers Brian Sabanal, Marion John Michael Achondo, Lief Erikson Gamalo, Pedro Alviola IV, and Mae Responte assessed UPMin’s local community’s knowledge, perception, and awareness on spiders' ecological and socio-economic benefits to reinforce the conservation of this invertebrate group. The paper is a result of UPMin’s Green Campus Initiative. Spiders have a significant role as beneficial predators, keeping the pest population—such as mosquitoes that spread dengue—in check. Their venom is also being studied to develop treatments for some diseases.
 |
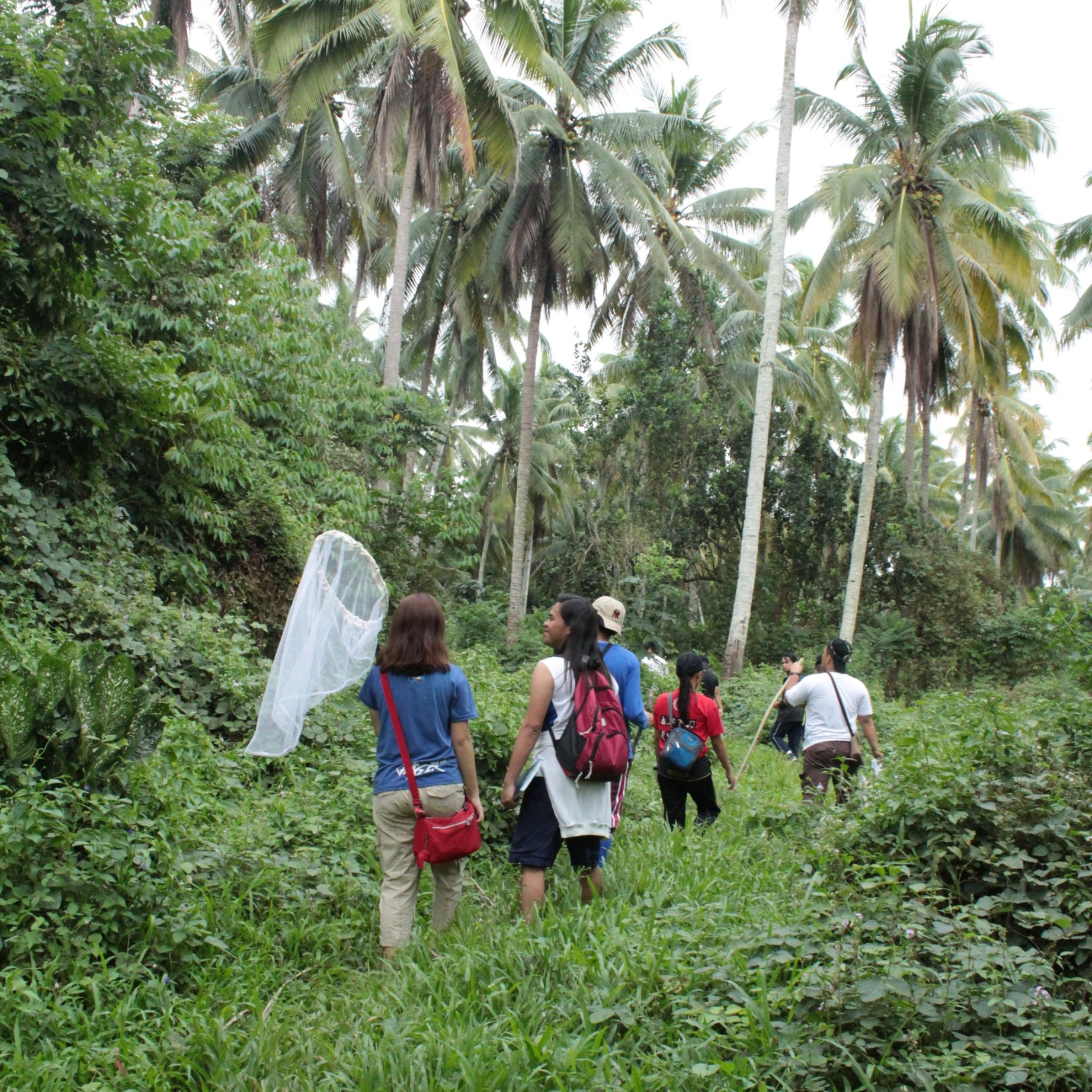 |
| A variety of spiders displayed in the research paper | The research team on fieldwork |
Research: ‘Eye in the sky’
See complete report here: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025326X22011717?fbclid=IwAR1bSHRotWOz-XXWUEQx6tTJr6lTdqcYVT8d6Ei66R345TaCs_FkSSzikz4
Marine Pollution Bulletin
Volume 186, January 2023, 114489
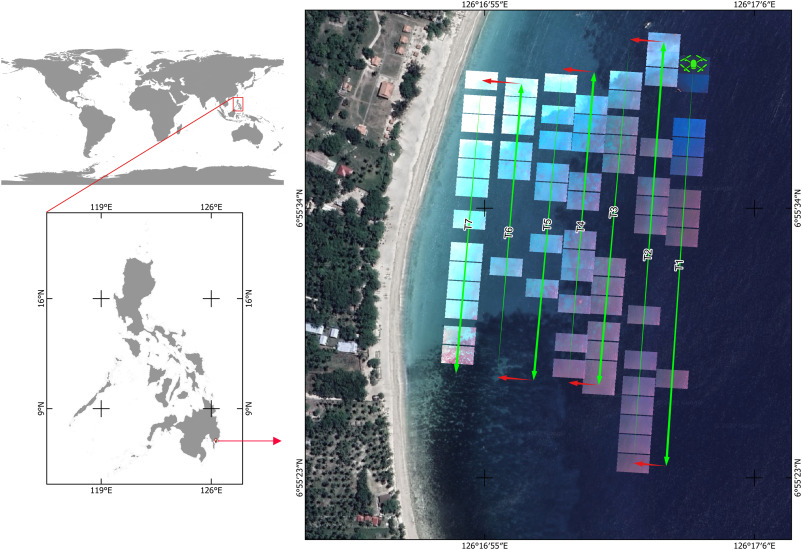
‘Eye in the sky’: Off-the-shelf unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) highlights exposure of marine turtles to floating litter (FML) in nearshore waters of Mayo Bay, Philippines
Neil Angelo S. Abreo, Remie M. AurelioJr, Vladimer B. Kobayashi, Kirsten F. Thompson
Received 20 October 2022, Revised 8 December 2022, Accepted 10 December 2022, Available online 20 December 2022, Version of Record 20 December 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114489 Get rights and content
Highlights
• Scarce data on marine litter and wildlife interaction needs to be addressed.
• Commercially-available UAVs are useful for litter and wildlife interaction research.
• Turtles are highly exposed to floating marine litter in nearshore waters.
• Improvements on the current methodology are needed.
Abstract
Litter is a serious threat to the marine environment, with detrimental effects on wildlife and marine biodiversity. Limited data as a result of funding and logistical challenges in developing countries hamper our understanding of the problem. Here, we employed commercial unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) as a cost-effective tool to study the exposure of marine turtles to floating marine litter (FML) in waters of Mayo Bay, Philippines. A quadcopter UAV was flown autonomously with on-board camera capturing videos during the flight. Still frames were extracted when either turtle or litter were detected in post-flight processing. The extracted frames were georeferenced and mapped using QGIS software. Results showed that turtles are highly exposed to FML in nearshore waters. Moreover, spatial dependence between FML and turtles was also observed. The study highlights the effectiveness of UAVs in marine litter research and underscores the threat of FML to turtles in nearshore waters.
More Articles...
Lock full review www.8betting.co.uk 888 Bookmaker
